Materials
Course slides (as PDFs):
- Introduction, part I, Introduction, part II
- Advanced DAG Encodings
- Attributes, part I, Attributes, part II
- DAG Construction
- DAG Ray Casting
- Compressed Shadow Volumes
- Compressed Shadow Maps
- Conclusion
The original .pptx files are available on Ulf Assarsson’s homepage, under the section “Publications”. The .pptx files are significantly larger, but retain the original videos/animations (which the PDFs do not).
A link to the CUDA ray-casting code will also appear in the following weeks.















Abstract
In this tutorial, we discuss voxel DAGs and multiresolution hierarchies, which are representations that can encode large volumes of data very efficiently. Despite a significant compression ration, an advantage of these structures is that their content can be efficiently accessed in real-time. This property enables various applications. We begin the tutorial by introducing the concepts of sparsity and of coherency in voxel structures, and explain how a directed acyclic graph (DAG) can be used to represent voxel geometry in a form that exploits both aspects, while remaining usable in its compressed from for e.g. ray casting.
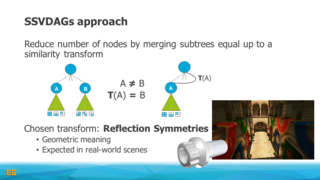
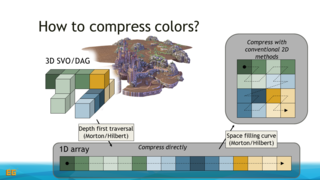
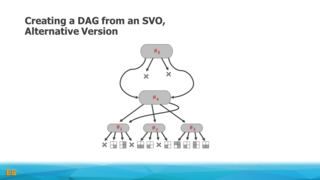
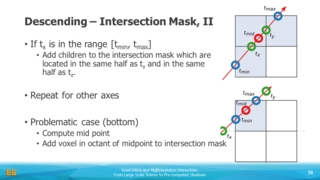
In this context, we also discuss extensions that cover the time domain or consider an advanced encoding strategies exploiting symmetries and entropy. We then move on to voxel attributes, such as colors, and explain how to integrate such information with the voxel DAGs. We will provide implementation details and present methods for efficiently constructing the DAGs and also cover how to efficiently access the data structures with e.g. GPU-based ray tracers.
The course will be rounded of with a segment on applications. We highlight a few examples and show their results. Pre-computed shadows are a special application, which will be covered in detail. In this context, we also explain how some of previous ideas contribute to multi-resolution hierarchies, which gives an outlook on the potential generality of the presented solutions.
Links
- Publication information and original submission at the Eurographics Digital Library.
Co-authors - Chalmers
Co-authors - CRS4
Co-authors - TU Delft
Errata
(Find anything inaccurate, any errors? Something worth pointing out? Send me an email!)

